Scientists develop first-of-its-kind antibody to block Epstein Barr virus
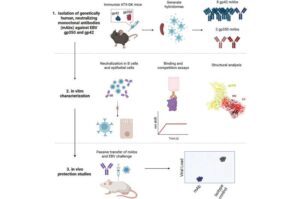
Fred Hutch Cancer Center scientists reached a crucial milestone in blocking Epstein Barr virus (EBV), a pathogen estimated to infect 95% of the global population that is linked to multiple types of cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and other chronic health conditions. Using mice with human antibody genes, the research team developed new genetically human monoclonal antibodies that prevent two key antigens on the surface of the virus from binding to and entering human immune cells.