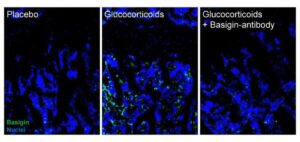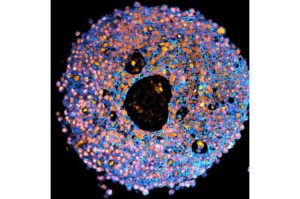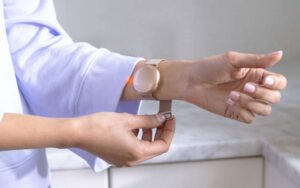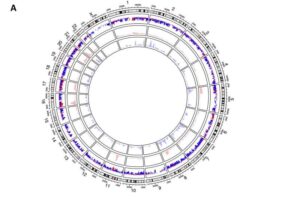
Spider-inspired magnetic soft robots could perform minimally invasive gastrointestinal tract procedures
A team of researchers at the University of Macau in China recently developed new soft magnetic robots that can climb inverted surfaces and move in complex environments, which could allow them to deliver drugs to specific locations in the GI tract.