MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano

Basivertebral nerve ablation provides early, sustained chronic low back pain relief
Chronic low back pain significantly affects quality of life for millions of people worldwide. Back pain makes it difficult to perform everyday tasks and is among the leading reasons why patients see their doctor.
Reprogrammed skin cells shed light on HIV-related cognitive impairment
Using participant skin cells reprogrammed into neurons, Weill Cornell Medicine researchers have identified genetic signatures associated with HIV infection that may contribute to the cognitive impairment that often occurs in people living with HIV, even when the virus is controlled.
New blood test shows extent of brain injury after stroke—and reveals treatment effects
Strokes are a medical emergency, yet imaging can capture only snapshots of how brain damage develops in the hours and days that follow. For many other organs, blood tests can indicate acute injury, but until now the brain has lacked a comparable marker. Researchers at LMU University Hospital and international partners report that a new blood biomarker, brain-derived tau (BD-tau), can track the extent of brain injury after ischemic stroke over time.
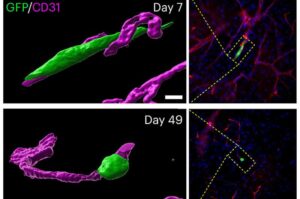
Dormant cancer cells can change shape to survive immune system attack
Cancer cells that have broken away from a primary tumor can lurk in the body for years in a dormant state, evading immune defenders and biding their time until conditions are ripe for establishing a new tumor elsewhere in the body, a process known as metastasis.

A sweat-based sensor may help improve sleep quality
University of Texas at Dallas researchers, in partnership with Texas-based biotech company EnLiSense, have demonstrated a pioneering wearable perspiration-based sensor that measures two key hormones that regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle.
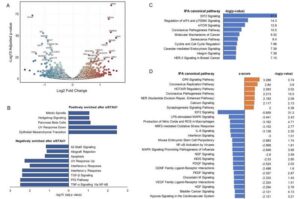
New ALS treatment target identified: STAUFEN-1 protein reduction protects brain cells from death
University of Utah researchers at the Pulst-Scoles Laboratory have discovered that reducing levels of the STAUFEN-1 protein can prevent neuron death caused by DNA damage and p53 activation in neurodegenerative diseases.
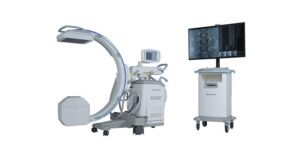
Proprio’s Fourth FDA Clearance Highlights Growing Shift to 3D Measurement in Spine Care
SEATTLE, Jan. 15, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Proprio, the surgical technology company pioneering real-time, AI-powered intraoperative guidance and data-driven surgical workflows, today announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted clearance for the “Picasso” feature. This marks the company’s fourth FDA-cleared capability within its Paradigm platform.
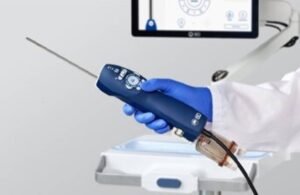
BD wins FDA nod for breast biopsy, tissue removal system
BD (NYSE: BDX)+
announced today that the FDA granted 510(k) clearance for its EnCore EnCompass breast biopsy and tissue removal system.
