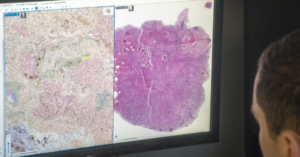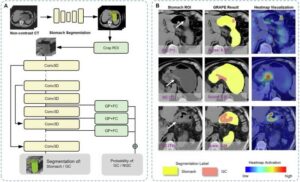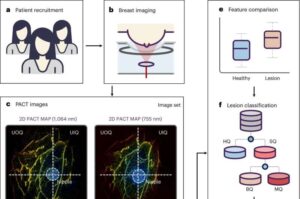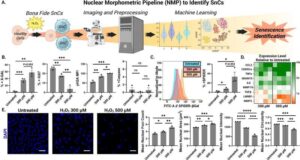
AI-assisted technique can measure and track aging cells
A combination of high-resolution imaging and machine learning, also known as artificial intelligence (AI), can track cells damaged from injury, aging, or disease, and that no longer grow and reproduce normally, a new study shows.