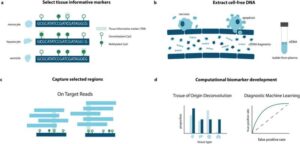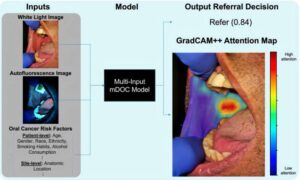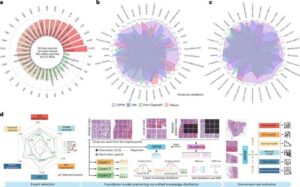
AI system delivers comprehensive cancer diagnosis
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) today launched SmartPath, a comprehensive artificial intelligence (AI) system designed to transform the entire pathology workflow for cancer care.