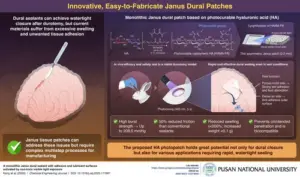
Pusan National University Researchers Develop Light-Activated Tissue Adhesive Patch for Rapid, Watertight Neurosurgical Sealing
Researchers develop an innovative dural patch that achieves rapid, watertight sealing of dural tears, boasting high biocompatibility