
Neurovalens wins FDA nod for weight management neurostim device
Neurovalens announced that it received FDA de novo approval for Modius Lean, its non-invasive neurotechnology for weight management.

Neurovalens announced that it received FDA de novo approval for Modius Lean, its non-invasive neurotechnology for weight management.

A new, soft, all-in-one, wearable system has been designed for continuous wireless monitoring of neonatal health in low-resource settings.
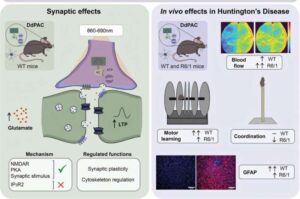
Synaptic plasticity—the brain’s ability to modify the connections between neurons to support learning—is one of the neural functions profoundly altered in Huntington’s disease, with a direct impact on brain function.
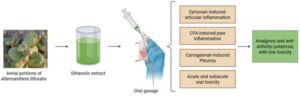
In Brazil, researchers from the Federal University of Grande Dourados (UFGD), the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), and São Paulo State University (UNESP) have conducted a study that confirmed the safety and anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-arthritic properties of the Joseph’s Coat plant (Alternanthera littoralis).

HeartBeam (Nasdaq:BEAT) announced today that it received FDA 510(k) clearance for its 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) synthesis software.

The Wearable Imaging for Transforming Elderly Care (WITEC) collaborative research project aims to develop the world’s first wearable ultrasound imaging system for continuous, real-time monitoring and personalised diagnosis of chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure.

The tiny opaque tube that Yonghui Ding holds up to the light in his laboratory looks like a bit of debris from a dismantled ballpoint pen.
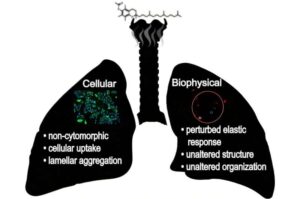
Researchers from the University of Windsor are using neutrons at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory to better understand symptoms associated with e-cigarette/vaping-associated lung injury (EVALI).
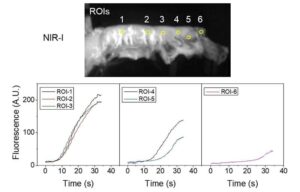
A cross-disciplinary research team has, for the first time, successfully applied NIR-II (1,000–3,000 nm) fluorescence video imaging during esophagectomy.
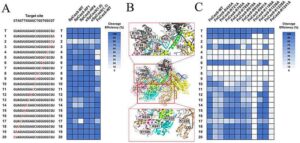
Liquid biopsy is increasingly recognized as a promising tool for cancer detection and treatment monitoring, yet its effectiveness is often limited by the extremely low levels of tumor-derived DNA circulating in the blood.