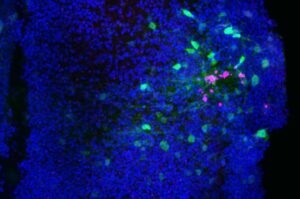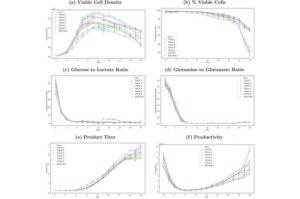
mRNA therapy could protect patients from radiation-induced skin damage caused by cancer treatment
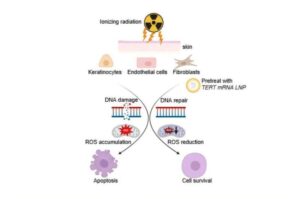
Researchers at Houston Methodist Research Institute have now discovered a promising new approach that can protect patients from radiation-induced skin damage during cancer treatment.