MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano
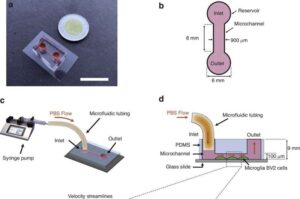
Portable device could help scientists track Alzheimer’s disease as it unfolds in real time
A team of researchers from Concordia University and McGill University has developed a “lab-on-a-chip” device that models how Alzheimer’s disease advances in the brain.
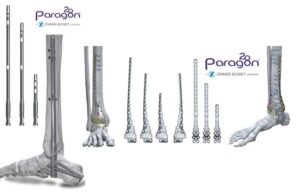
Zimmer Biomet launches foot, ankle trauma systems
Zimmer Biomet (NYSE: ZBH)+
announced that it launched two new solutions for complex foot and ankle trauma.
New method may detect infectious tuberculosis in the air
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet, in collaboration with colleagues in South Africa, have investigated whether tuberculosis can be traced in exhaled air. The results, published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases, show that a new method may help identify people with infectious tuberculosis directly in primary care.

Improved genetic tool reveals hidden mutations that can drive cancer
Researchers have refined a powerful DNA sequencing tool that can uncover hidden mutations that occur naturally in our bodies as we age. In the largest study to date, they have used the tool to provide insights into the earliest steps of cancer development and the role of mutations in healthy tissue.
A radiotheranostic approach designed to combat aggressive cancers
UCLA scientists, together with a team of international collaborators, have identified a promising new treatment strategy that can detect, kill and reprogram aggressive, treatment-resistant tumors like osteosarcomas and glioblastoma.
Bunkerhill Health Receives FDA Clearance for the First-Ever AI Solution to Detect Mitral Annular Calcification
SAN FRANCISCO, Oct. 8, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Bunkerhill Health today announced that it has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance for Bunkerhill MAC, the first artificial intelligence algorithm to detect and quantify mitral annular calcification (MAC). The algorithm runs on routine, non-gated chest CT scans.
Prytime Medical Devices Receives World’s First Extended Duration FDA 510(k) Clearance for pREBOA-PRO™ Catheter
BOERNE, Texas, Oct. 8, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Building once again on their first mover position as a leader in endovascular hemorrhage control and resuscitation, Prytime Medical Devices, Inc. (Prytime) this week announced a new FDA 510(k) clearance for their flagship pREBOA-PRO™ Catheter.

Synchrony Medical Launches LibAirty™ Airway Clearance System in the U.S., Offering a New Standard for At-Home Respiratory Care
JERSEY CITY, N.J. and OR YEHUDA, Israel, Oct. 8, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Synchrony Medical, a medical technology company dedicated to transforming respiratory care, announced today the launch of its LibAirty™ Airway Clearance System in the United States. The launch marks an important step forward for people living with chronic lung disease, providing access to advanced at-home therapy designed to improve daily breathing, reduce exacerbations and hospitalizations, and enhance quality of life.
