MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano
Seno Medical’s Next-Generation Imagio® Imaging System Obtains European Union (EU) Medical Device Regulation (MDR) CE Mark Certification
The CE Mark certification enables Seno Medical to market and sell the latest version of its Imagio® Imaging System with opto-acoustic, sound, and artificial intelligence in the European Union.
New ‘lab-on-a-disc’ device paves the way for more automated liquid biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles shed by cells that carry important molecular “clues” about the cell’s identity and condition.
Epistasis study uncovers genetic interactions linked to heart disease
Euan Ashley’s lab explores the intricate interactions of gene variants. Tiny “typos,” or genetic mutations, can sneak into segments of DNA. Many of these are harmless, but some can cause health problems. Two or more genes can team up and change the outcome of a physical or molecular trait. This phenomenon, known as epistasis, occurs through complex interactions between genes that are functionally related—such as those that support protein creation.
Fecal transplant can improve response to immunotherapy in advanced kidney cancer
An Italian study published in Nature Medicine provides compelling evidence that fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) can enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy in patients with advanced metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC).
Glowing bacterial sensors detect gut illness in mice before symptoms emerge
University of British Columbia researchers have engineered gut bacteria that dim their fluorescent glow in the presence of illness. Their findings could improve how we diagnose problems in the gut by using bacteria that already live there. The work appears in Cell.
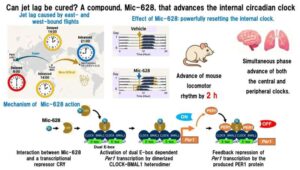
No more jet lag? Scientists discover oral compound that helps ‘reset’ the body clock forward
A Japanese research team has discovered a new compound that can advance the body’s internal clock—offering hope for faster recovery from jet lag and better adaptation to night-shift work.
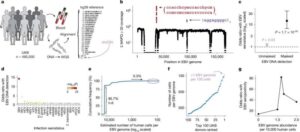
DNA research uncovers 22 genes that could put people at risk of long-term health conditions
Baylor College of Medicine researchers are part of a collaborative research group with AstraZeneca and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center that have identified 22 genes which increase the risk of developing a range of chronic conditions following a common viral infection.
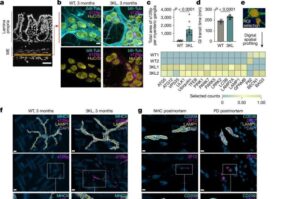
Targeting the gut’s immune system could tackle early stages of Parkinson’s
New research reveals how Parkinson’s spreads from the gut to the brain, with the help of immune cells—offering a new potential therapeutic strategy—in a study in mice led by scientists at the UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL (University College London).
