MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano
Two genes found to suppress colorectal cancer spread in preclinical models
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, and among all cancers, colorectal cancer ranks second in mortality, responsible for more than 900,000 deaths in 2020.

Experimental drug repairs DNA damage caused by common diseases
Cedars-Sinai scientists have developed an experimental drug that repairs DNA and serves as a prototype for a new class of medications that fix tissue damage caused by heart attack, inflammatory disease or other conditions.

A common childhood virus can drive bladder cancer development
Tackling a common childhood virus could open the door to preventing bladder cancer, according to new research.
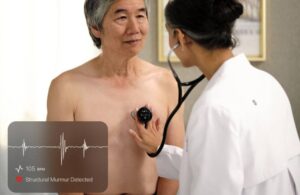
Eko reports reimbursement win for AI-powered cardiac disease detection
Eko Health announced today that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has finalized national payment for its Sensora platform.

Insulet makes Omnipod 5 available with Dexcom G7 15 Day CGM
Insulet (Nasdaq:PODD) today announced immediate compatibility between its Omnipod 5 system and the Dexcom (Nasdaq:DXCM) G7 15 Day CGM.

Medtronic begins full commercial rollout of MiniMed 780G with Instinct sensor made by Abbott
Medtronic (NYSE: MDT)+
today announced the full U.S. launch for its Instinct sensor, made by Abbott, paired with the MiniMed 780G pump.

FDA accepts MannKind sNDA for autoinjector that treats edema
MannKind (Nasdaq:MNKD) announced that the FDA accepted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for its Furoscix ReadyFlow autoinjector.

Cleveland Diagnostics’ IsoPSA secures FDA approval for prostate cancer
The decision is supported by evidence from a clinical study and data from supporting analytical validation trials.
