MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano
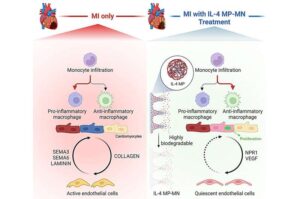
Healing the heart after a heart attack with a biodegradable patch
A new patch developed by Texas A&M University researcher Dr. Ke Huang may offer a way to help the heart heal after a heart attack. The patch uses a unique microneedle system to deliver a therapeutic molecule directly to damaged heart tissue, promoting repair and improving heart function without affecting the rest of the body.
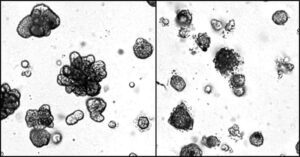
Precision therapy could stop breast cancer at the source
Researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine have identified a promising new therapy for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which is among the most aggressive and difficult-to-treat forms of the disease.
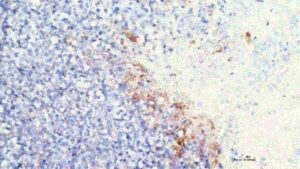
CRISPR breakthrough reverses chemotherapy resistance in lung cancer
In a major step forward for cancer care, researchers at ChristianaCare’s Gene Editing Institute have shown that disabling the NRF2 gene with CRISPR technology can reverse chemotherapy resistance in lung cancer. The approach restores drug sensitivity and slows tumor growth. The findings are published in the journal Molecular Therapy Oncology.
Gene ‘switch’ reverses Alzheimer’s risk in experimental model
University of Kentucky researchers have developed a new experimental model that could point the way toward more effective Alzheimer’s disease treatments by targeting one of the brain’s most important genes for risk and resilience.
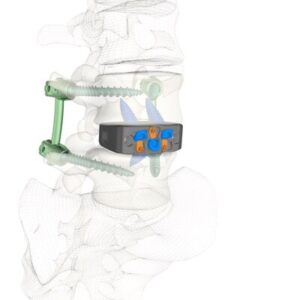
Zavation Medical Products Announces First Implantations of Varisync® ALIF NanoPrime™
FLOWOOD, Miss., Nov. 15, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Zavation Medical Products, LLC (“Zavation”), a leading innovator in spinal device technology, announces the first successful implantations of the Varisync® ALIF NanoPrime™ System, a next-generation stand-alone ALIF system featuring Zavation’s proprietary titanium ion bond technology.

Avicenna.AI Launches AVI Seamless Platform for Medical Imaging AI
New platform is designed to enable fast, scalable access to a wide range of AI imaging solutions

FDA grants label expansion for BrainsWay Deep TMS to treat MDD
The clearance is based on data that included real-world evidence from 1,120 adolescents who received treatment at US TMS centres.

Renu MedTech introduces tubeless insulin patch pump in India
Renu MedTech today unveiled InsuPatch, its tubeless insulin patch pump designed specifically for advancing diabetes care in India.
