Ultrasmall theranostic nanozyme offers new hope for abdominal aortic aneurysm management
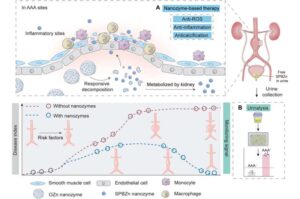
A team led by Professor Hui Wei, a pioneer in nanozyme research at Nanjing University, has unveiled an ultrasmall theranostic nanozyme with the potential to transform the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)—a highly lethal vascular disease with limited therapeutic options.