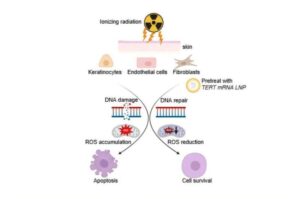
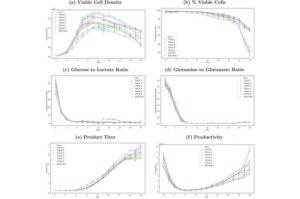
Affordable microscope speeds up malaria diagnosis with AI
Engineers at Stanford University have developed a high-efficiency, battery/solar-operated, autonomous microscope with integrated artificial intelligence that automatically diagnoses malaria in blood smears