MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano
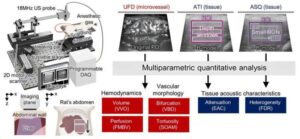
Steatotic liver disease precisely assessed using 3D ultrafast vascular ultrasound
Steatotic liver disease (commonly called fatty liver disease) progresses silently. Even in the absence of noticeable symptoms, changes begin to unfold inside the liver.
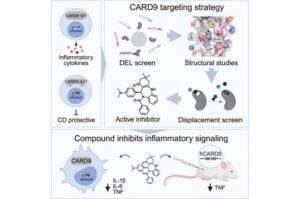
Small molecules could treat Crohn’s disease by mimicking a protective gene variant
An estimated 3 million Americans have an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. But a lucky few individuals are far less likely to develop IBD because they have a rare variant of a gene called CARD9. This protective gene variant prevents the long-term digestive tract inflammation that can cause tissue damage and lead to disease.
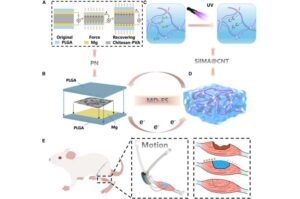
Researchers develop biodegradable, self-powered electrical stimulator for muscle repair
A research team led by Prof. Bai Shuo from the Institute of Process Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has pioneered a fully biodegradable, self-powered implantable electrical stimulation system designed to enhance muscle repair.

New coffee chemicals show promise for managing type 2 diabetes
Coffee may do more than boost energy. New research suggests that certain compounds found in roasted coffee beans could help slow how quickly sugar enters the bloodstream, a finding that could one day support new foods aimed at managing type 2 diabetes.
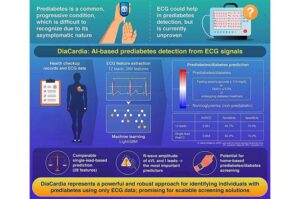
AI model detects prediabetes using ECG data without need for blood tests
DiaCardia, a novel artificial intelligence model that can accurately identify individuals with prediabetes using either 12-lead or single-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) data, has been developed. This breakthrough holds promise for future home-based prediabetes screening using consumer wearable devices, without requiring invasive blood tests.
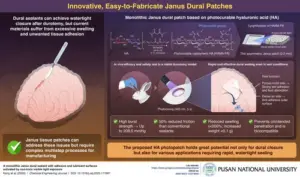
Pusan National University Researchers Develop Light-Activated Tissue Adhesive Patch for Rapid, Watertight Neurosurgical Sealing
Researchers develop an innovative dural patch that achieves rapid, watertight sealing of dural tears, boasting high biocompatibility

New method predicts asthma attacks up to five years in advance
Researchers at Mass General Brigham and Karolinska Institutet have identified a new method to predict asthma exacerbations with a high degree of accuracy.

‘Revoice’ device gives stroke patients their voice back
Researchers have developed a wearable, comfortable and washable device called Revoice that could help people regain the ability to communicate naturally and fluently following a stroke, without the need for invasive brain implants.
