MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano

Spray away infections: New device delivers antibiotics via mist, alleviating risks of side effects
A University of Missouri researcher has unveiled a safer, smarter way to fight drug-resistant infections.
Self-regulating living implant could end daily insulin injections
A pioneering study marks a major step toward eliminating the need for daily insulin injections for people with diabetes.
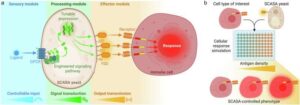
Yeast cells can be used for rapid testing of cancer immunotherapy
An international research team with strong participation from DTU has developed a new biotechnological platform that makes it possible to test and understand advanced cancer treatments much faster and cheaper than before
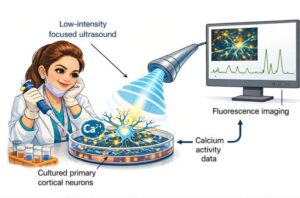
A new way to communicate with neurons using focused ultrasound stimulation
I still vividly remember the first time we observed neurons responding not to audible sound, but to concentrated, precisely calibrated ultrasonic pulses.

Unexpected partial recovery of natural vision observed after intracortical microstimulation in a blind patient
A patient with complete blindness caused by irreversible optic nerve damage partially recovered natural vision after participating in a clinical trial of electrical stimulation of the visual cortex conducted by researchers.
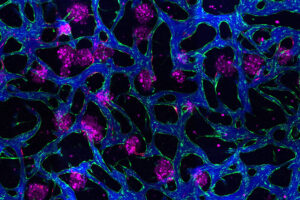
New tissue models could help researchers develop drugs for liver disease
Two models more accurately replicate the physiology of the liver, offering a new way to test treatments for fat buildup.

SMART launches new Wearable Imaging for Transforming Elderly Care research group
WITEC is working to develop the first wearable ultrasound imaging system to monitor chronic conditions in real-time, with the goal of enabling earlier detection and timely intervention.
Quest launches flow cytometry MRD test for myeloma
Quest expects the new blood test will support response monitoring in clinical trials.
