MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano
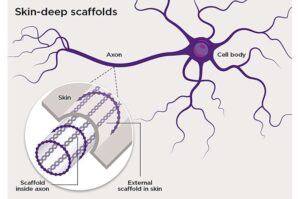
Pleasure and pain: Tiny worm reveals secret to protecting skin sensations
A tiny roundworm has helped University of Queensland scientists uncover minuscule structures in skin tissue that may protect the body’s ability to feel temperature, touch and pain. The research is published in Science Advances.

AI tool predicts six-month risks for cancer patients after heart attack
Cancer patients who suffer a heart attack face a dangerous mix of risks, which makes their clinical treatment particularly challenging. As a result, patients with cancer have been systematically excluded from many clinical trials and available risk scores. Until now, doctors had no standard tool to guide treatment in this vulnerable group.
Designing the future of metabolic health through tissue-selective drug delivery
Founded by three MIT alumni, Gensaic uses AI-guided protein design to deliver RNA and other therapeutic molecules to specific cells or areas of the body.

FDA clears Spectrum Dynamics’ Veritas.AI platform
Veritas.AI is designed to advance the functionality of Spectrum Dynamics’ VERITON-CT scanner for nuclear imaging.
KORU Medical receives FDA clearance for FreedomEDGE infusion system
Rystiggo is administered weekly, 3ml to 6ml over 15 to 30 minutes for six weeks.
GRAIL Submits FDA Premarket Approval Application for the Galleri® Multi-Cancer Early Detection Test
MENLO PARK, Calif., Jan. 29, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — GRAIL, Inc. (Nasdaq: GRAL), a healthcare company whose mission is to detect cancer early when it can be cured, today announced the submission of the final module of the Premarket Approval (PMA) application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its Galleri® multi-cancer early detection (MCED) test. The FDA designated the test as a Breakthrough Device in 2018.
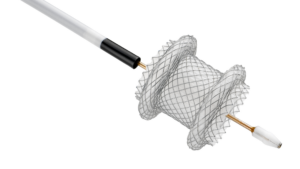
Zeus Launches PFX™ Platform and Introduces PFX Flex™ Sub-Lite-Wall™, Advancing the Future of Catheter Innovation
ORANGEBURG, S.C., Jan. 29, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Zeus, a global leader in advanced polymer solutions, today announced the launch of PFX™, a breakthrough platform designed to advance catheter innovation with a focus on performance, design flexibility, and sustainability.

NEXTBIOMEDICAL Secures Health Canada Approval for Nexsphere-F™ in Musculoskeletal Pain Embolization
SEOUL, South Korea, Jan. 29, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — NEXTBIOMEDICAL CO., LTD. (KOSDAQ: 389650), an innovative medical device company based in South Korea, announced today that Nexsphere-F™, the company’s novel fast resorbable microsphere for musculoskeletal pain embolization has received approval from Health Canada.
