MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano
Zoll wins CE mark for new Zenix monitor/defibrillator
Zoll announced today that it received CE mark approval under the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) for its Zenix monitor/defibrillator.

Vesalio Expands International Neurovascular Portfolio with CE Mark of NeVa VS and NeVa 3.0 mm and Receives Additional FDA 510(k) Clearance for its Aspiration Catheters
PLANO, Texas, Feb. 10, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Vesalio, a global leader in vascular intervention, today announced CE Mark certification and the European commercial launch of two new neurovascular devices: NeVa™ VS, for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH), and the NeVa™ 3.0 mm Thrombectomy System for stroke. In addition, the Company received an additional U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) clearance expanding the indications of its neurovascular and peripheral aspiration catheters to include distal access.

New artificial intelligence tool diagnoses masked hypertension
Researchers at the University of Arkansas have developed an artificial-intelligence diagnostic tool to detect masked hypertension.
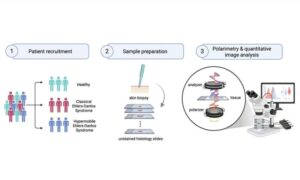
Polarized-light imaging shows potential for distinguishing Ehlers–Danlos subtypes
In a recent study by researchers in Toronto (Canada), scientists tested an optical method called Mueller matrix polarimetry to address a diagnostic gap.

Affordable microscope speeds up malaria diagnosis with AI
Engineers at Stanford University have developed a high-efficiency, battery/solar-operated, autonomous microscope with integrated artificial intelligence that automatically diagnoses malaria in blood smears

Robotic medical crash cart eases workload for health care teams
Research on their new robotic crash cart (RCC)—a robotic version of the mobile drawer unit that holds supplies and equipment needed for a range of medical procedures.
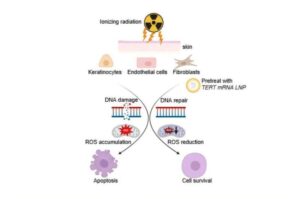
mRNA therapy could protect patients from radiation-induced skin damage caused by cancer treatment
Researchers at Houston Methodist Research Institute have now discovered a promising new approach that can protect patients from radiation-induced skin damage during cancer treatment.
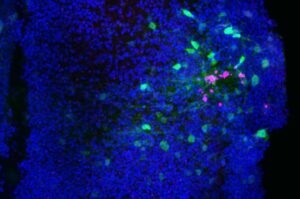
Controlled ‘oxidative spark’ may serve as a surprising ally in brain repair
In the future, more targeted strategies that dampen damaging, chronic oxidative stress while preserving—or even harnessing—these short-lived pro-healing signals could open new avenues to promote brain repair.
